Pinnacles loop walking track
Pambula-Haycock area in Beowa National Park
Overview
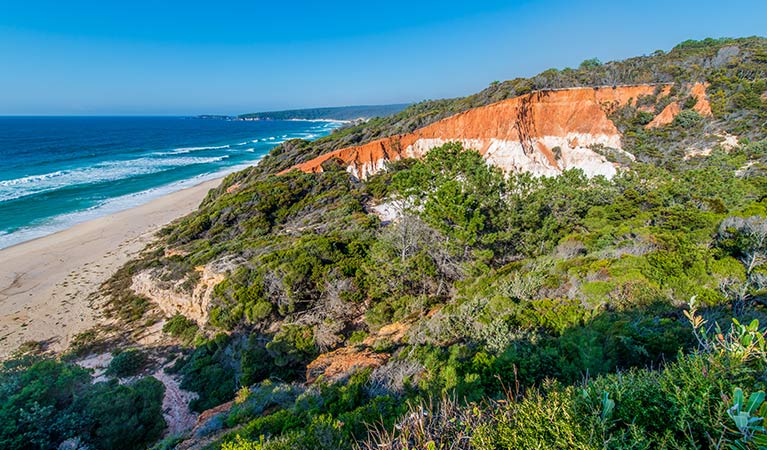
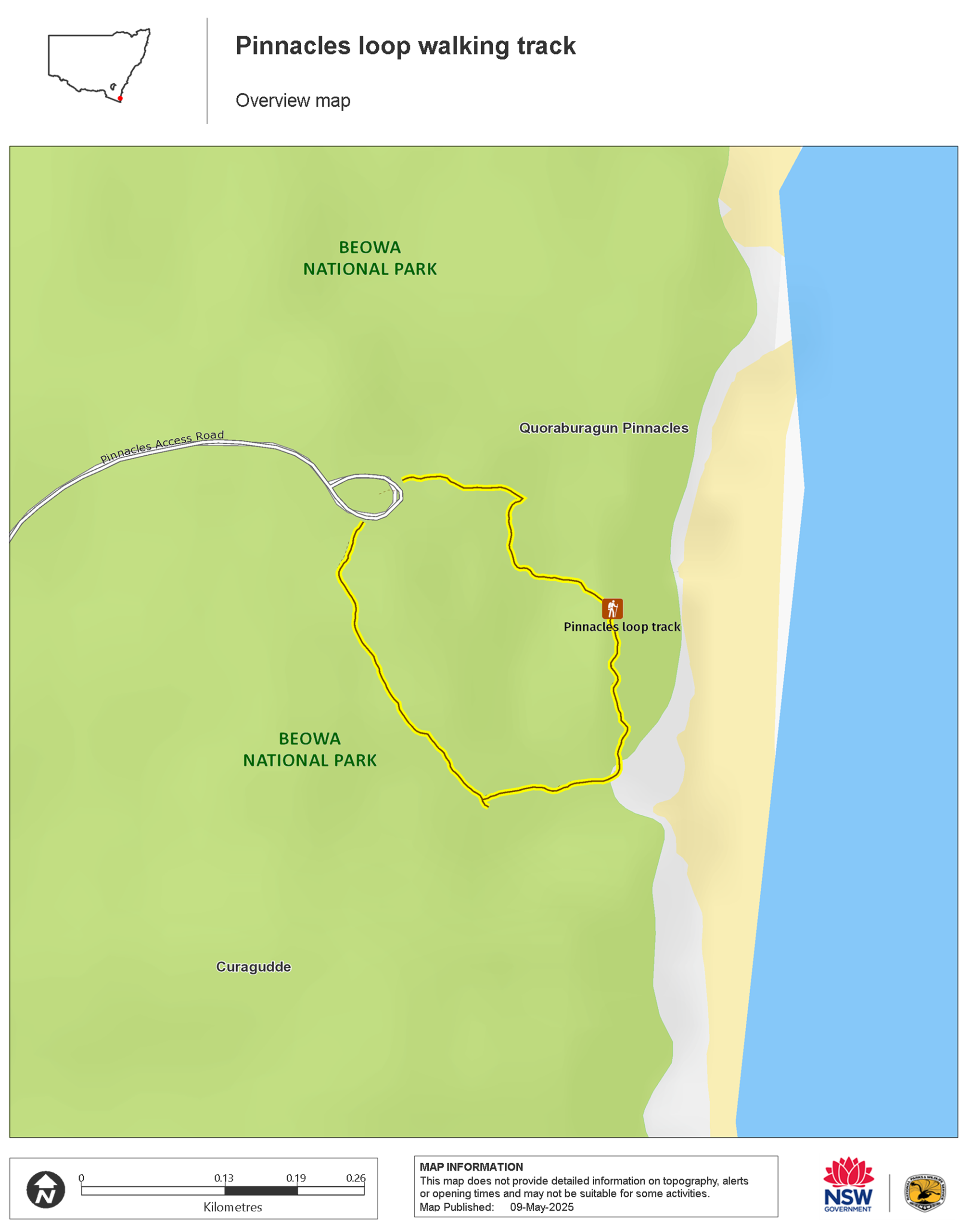
Pinnacles loop walking track in Beowa National Park is an easy walk with two lookout points from which you can view the Pinnacles erosion feature.
- Where
- Pambula-Haycock area in Beowa National Park in South Coast
- Accessibility
- Hard
- Distance
- 1.1km loop
- Time suggested
- 20 - 40min
- Grade
- Grade 3
- Please note
- It’s a good idea to put sunscreen on before you set out and remember to take a hat and drinking water
- Remember to take your binoculars if you want to go birdwatching or whale watching
Pinnacles loop walking track is a pleasant, easy walk that meanders through the woodland and heath of the NSW Far South Coast region. With beautiful coastal views south to Lennards Island and north to Haycock Point, it’s an easy stroll for all the family in Beowa National Park, a short drive south of Pambula.
There are two lookouts along this gently undulating walking track that make ideal spots to view the fascinating Pinnacles formation – a spectacular erosion feature that consists of cliffs of soft white sands capped with a layer of red gravel clay. It was deposited during the Tertiary geological period – up to 65 million years ago.
Large areas of pine trees can also be seen between the eucalypts, and NPWS has been working to return the area back to its natural state.
Map
Map legend
Local alerts
For the latest updates on fires, closures and other alerts in this area, see https://uat.nswparks.cloud/things-to-do/walking-tracks/pinnacles-loop-walking-track/local-alerts
General enquiries
- National Parks Contact Centre
- 7am to 7pm daily
- 1300 072 757 (13000 PARKS) for the cost of a local call within Australia excluding mobiles
- parks.info@environment.nsw.gov.au
Park info
- in the Pambula-Haycock area of Beowa National Park in the South Coast region
The Pambula-Haycock area of Beowa National Park is always open but may have to close at times due to poor weather or fire danger.
Visitor info
All the practical information you need to know about Pinnacles loop walking track.
Maps and downloads
Learn more
Pinnacles loop walking track is in Pambula-Haycock area. Here are just some of the reasons why this park is special:
Aboriginal culture

The Yuin People are the Traditional Owners and Custodians of Beowa National Park and they have a long and complex relationship with the coastal environment. Some of the best preserved mounded middens on the east coast of Australia are found in the park along the Pambula River. These middens contain the shells of oysters, mussels and sometimes the bones of sea and land mammals—collected by Aboriginal people from the rock platforms, reefs and estuaries along the park’s coastline.
- Severs Beach Severs Beach, in Beowa National Park in the whale watching town of Eden on NSW’s Sapphire Coast, offers Aboriginal heritage, fishing, beach walks and more.
- Traditional weaving workshop: Beowa Get creative on a traditional weaving workshop in Beowa National Park, halfway between Pambula and Eden. Learn Aboriginal weaving techniques and see how these ancient skills carry a strong connection to Aboriginal culture.
Rocks tell a story
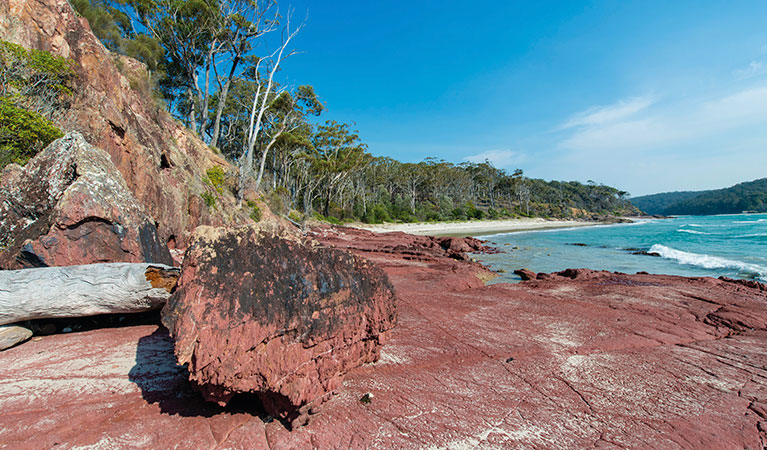

The park’s stunning rock formations, inlets and headlands are the result of extensive geological folding. Most of Beowa National Park lies on red, brown and green shales, sandstones, siltstones and quartzites. These were formed in the Devonian period around 360 million years ago, before dinosaurs roamed the earth. You can see these rock types exposed along the cliffs and headlands. The Devonian period is known as The Age of Fishes and internationally-significant fish fossils have been found in several places along the park’s coastline.
- Haycock Point to Barmouth Beach walking track The walk from Haycock Point to Barmouth Beach in Beowa National Park takes in whale watching, scenic coastal views, wildlife and birdwatching opportunities.
- Pambula River kayaking tour Experience Beowa National Park from the crystal-clear waters of the Pambula River on this exciting guided kayaking tour with Navigate Expeditions.
Refuge for threatened species

Several threatened species take refuge in the Pambula-Haycock area. North of Pambula River there's an important population of yellow-bellied gliders—listen carefully for their trademark crackles and shrieks. Around 50 native mammals and nearly 150 species of birds have been recorded in Beowa National Park. This includes 1 critically endangered bird, 4 endangered animal species and 25 vulnerable species.
- Haycock Point to Barmouth Beach walking track The walk from Haycock Point to Barmouth Beach in Beowa National Park takes in whale watching, scenic coastal views, wildlife and birdwatching opportunities.
- Pambula River kayaking tour Experience Beowa National Park from the crystal-clear waters of the Pambula River on this exciting guided kayaking tour with Navigate Expeditions.
Plants and animals protected in this park
Animals
-

Australian pelican (Pelecanus conspicillatus)
The curious pelican is Australia’s largest flying bird and has the longest bill of any bird in the world. These Australian birds are found throughout Australian waterways and the pelican uses its throat pouch to trawl for fish. Pelicans breed all year round, congregating in large colonies on secluded beaches and islands.
-

Australian fur seal (Arctocephalus pusillus doriferus)
The largest fur seal, Australian fur seals are found in isolated rocky outcrops and islands along the NSW coast. They come ashore to form breeding colonies and can often be seen at Barunguba Montague Island Nature Reserve.

